New France - area colonized by France in North America
New France was the first French colonial Empire, one that lasted from 1534–1763. Today it is a major theme in the histories of the Kingdom of France, Haiti, Canada, and the United States.
Understand
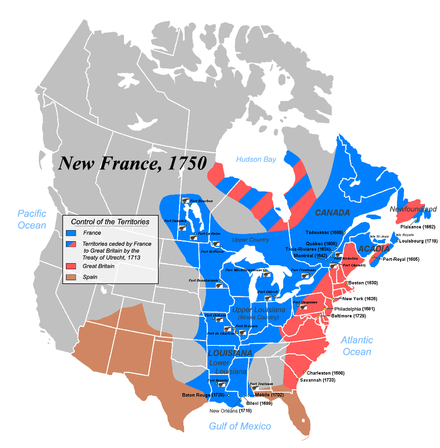 The History of New France spans more than two hundred years and includes most of the Eastern half of North America plus the Caribbean.
The History of New France spans more than two hundred years and includes most of the Eastern half of North America plus the Caribbean.
In general the story of the French colonial experiment is that, unlike the Spanish Empire, the French found no existing indigenous empires to plunder or major deposits of minerals to exploit, and unlike the English colonies nearby, very few French men and women came to the Western Hemisphere to settle.
The French colonies were primarily concerned with the lucrative fur trade in the north and with plantation slavery in the south. French relations with indigenous peoples were generally good, or at least better than the Spanish and English, with the notable exception of a bitter enmity with the Iroquois Confederacy.
The French controlled two of North America's greatest rivers, the St. Lawrence and the Mississippi and had numerous indigenous allies, yet were ultimately ejected from North America by the British. What brought the French Empire down was the population mismatch with the growing English settlements and Britain's superior ability to move its military forces by sea. Several times major French strongholds like Quebec and Louisbourg were captured by the British only to be returned following the result of negotiations were North America was an afterthought compared to European developments. The final blow came in 1759 with the capture of Quebec and Montreal, and in 1763 France relinquished all claims north of the Caribbean except for tiny Saint Pierre and Miquelon.
From this point on, the history of continental North America is the history of the British Empire and its transformation into the present-day countries of the United States and Canada as well as the transformation of the Spanish Empire into Mexico and the interaction of Mexico and remaining Spanish claims with the emerging Anglo-American nations.
The French briefly had the opportunity to revive their continental North American empire when Napoleon I got much of the Louisiana region back form Spain, but he almost immediately sold it to the United States, ushering in the era of American westward expansion. Napoleon tried a little harder to hold onto Haiti - at the time an incredibly lucrative slavery based plantation economy - but eventually had to give up on that as well in the face of a slave uprising that gave rise to the modern nation of Haiti. This failure by the French (and success by the Haitians) concluded the French chapter of North American history (excepting a brief foray into Mexico in the 1870s and a few small islands).
Regions
After being re-organized in 1717, the provinces of New France were:
- Acadia (l'Acadie): today Maine and Atlantic Canada
- Canada (le Canada):, basically the drainage basin of the St. Lawrence River, today Quebec, Southern Ontario and Upstate New York, plus:
- the Pays d'en haut or "up country": today Northern Ontario, the upper Midwest, and parts of Manitoba, where France did not control the territory but did have influence with the local indigenous peoples
- Louisiana (la Louisiane): basically the drainage basin of the Mississippi River, including all of the Southern States west of the Appalachian Mountains, and the lower Midwest (the "Illinois Country"). Theoretically, it also included the Great Plains and Mountain West states, but France never had a permanent presence there.
Destinations
Itineraries
The Chemin du Roy (King's Way) is an historic road (finished 1737) that links Quebec City to Montreal. Although the modern tourist signage nowadays ends at Repentigny, one can continue into Montreal on the historic route via Gouin Boulevard_._
Historic sites and towns
- Fort Charlesbourg Royal site of unsuccessful French settlement of 1541 to 1543, now in Quebec City.
- Tadoussac site of failed French settlement of 1600.
- Saint Croix Island the preserved site of the failed French settlement of 1604. Near Calais (Maine).
- Habitation at Port-Royal French settlement from 1605 to 1613 (near Annapolis Royal)
- Quebec City first successful settlement in New France, founded 1608, and capital of New France from when it become at royal colony in 1663 until it's capture in the famous siege of 1759.
- Mount Desert Island -- spotted in 1604 by Champlain, with a Jesuit mission established in 1613. Home of the majority of Acadia National Park.
- Trois-Rivières founded by French settlers in 1634.
- Montreal a French presence dating to the mission of Ville Marie in 1642.
- "Fort Saint Louis" [sic] - first location of an unamed French settlement of 1685, the first in present-day Texas, which was only later called by the rather grand name of "Fort Saint Louis".
- Detroit founded by French settlers in 1701, but with few French traces remaining.