Basketball in North America
Basketball in North America
Basketball is one of the most popular team sports in North America, both as a spectactor sport and as an activity, and the second most popular sport in the world, only after soccer. The top professional league, the National Basketball Association (NBA) is among the "Big 4" of North American sports leagues when it comes to popularity and revenue. The others are the National Football League, National Hockey League and Major League Baseball. The NBA is head and shoulders above all other professional basketball leagues, and thus attracts the best talent from all over the world.
Understand

History
The game was invented in December 1891 by the Canadian-American James Naismith, who was a college professor in Springfield, Massachusetts. He wanted to come up with a team sport that could be played indoors during the winter when the weather didn't allow for popular outdoor sports like rugby, football, soccer or baseball. He used soccer balls for the game; proper basketballs were invented several decades later. Naismith also intended the game to limit contact between players, fixing the goal at a height then thought to be hard to reach even by jumping as he observed a lot of physical contact going in the contest close to the goal in other sports. There are conflicting interpretations whether this was due to the high injury risk associated with various codes of football or ice hockey at the time or religious prudery.
The color line in professional basketball was broken in the NBA's second season (1947/48), when the league signed its first non-white player, Japanese-American Wataru Misaka. By the 1950s African-American players became a common sight in the league. Now, almost three out of four NBA players are African-American. A significant minority of non-American players are black or mixed-race — for example, two-time MVP Giannis Antetokounmpo (Greece) is the son of Nigerian immigrants, and three-time Defensive Player of the Year Rudy Gobert (France) has a black father and white mother. While the demographics of the fans also skew somewhat in favor of black people, it is far less noticeable than among the players.
The NBA draws most of the top players from throughout the world. Two major events at the end of the 1980s brought this about: the collapse of the Soviet Union, and the decision of FIBA, the sport's international governing body, to allow NBA players to compete in the Olympics. Today, a bit over 20% of the league's players were born outside the U.S. The largest share has traditionally come from Europe, but African countries are producing an increasing number of players. Many other countries are represented in the league, including Argentina, Australia, Brazil, and Canada. The Spanish presence is large enough that Spaniards now call their men's national team La ÑBA.
Rules and gameplay
Basketball is played by two teams, each having 5 players on the court. The objective is to put (by throwing) the basketball through the basket or hoop mounted at the rear of the opposing team's side, thereby scoring points. Another objective is preventing the opposing team from putting the ball through the hoop on their side. The hoops are mounted 10 ft (about 3 m) above ground to prevent goaltending. The team usually gets two points for putting the ball through the hoop; this is called a field goal. If it's thrown from further away, behind the three-point line, the team gets three points. Actions against the rules fall under two categories: violations and fouls. Most fouls occur as a result of personal contact with another player, and usually results in the ball being turned over to the opposing team. A player who has committed 6 fouls in the NBA or WNBA, or 5 fouls in the Olympics and NCAA, is fouled out, meaning that (s)he must be substituted off and cannot take part in the remainder of the game.
When a player commits a foul against a player from the opposing team who is attempting a goal, the fouled player may attempt throw the ball into the hoop while everyone else is standing still. This is called a free throw, and is worth one point if the throw is successful. In most cases, a player is entitled to take two or three free throws, depending on where the shot attempt was made; if you hear that a player is shooting "one-and-one", then the player will get another opportunity if the first free throw scores. (The "one-and-one" is now used only in two US rule sets—college men's, and high schools for both sexes.) If the player that is being fouled scores a goal, one free throw is awarded so the player has the chance to score an extra point. Two free throws are also awarded for all defensive fouls regardless of whether the fouled player is attempting a shot once a team has accumulated a certain number of fouls in a certain period, which is 5 per quarter in the NBA, WNBA, Olympics, and NCAA women's play, and 7 per half in NCAA men's and high school play. The team with most points when the time is up wins the game.
Game duration varies between leagues. In the NBA, games are played in four quarters, each taking 12 minutes. The WNBA is also played in quarters, but each lasts only 10 minutes. College games are the same length as WNBA games, but the timing conventions are different for men's and women's play. Men's games are played in 20-minute halves, while women's games use 10-minute quarters. Games at the Olympics and other international tournaments are played in 10-minute quarters. Youth games use shorter periods still; for example, US high school games are played in 8-minute quarters. If the score is even when the time is up, overtime periods of five minutes (4 in US high schools) are played until a winner emerges. Like hockey, and unlike soccer, the clock is stopped when the play isn't active, so games take more time than actual playing time. The shot clock is equally important to the pacing of a basketball game. Set at 24 seconds in professional and Olympic basketball, and 30 seconds in college basketball, the shot clock marks the time that the offensive team has to set up and make a shot at the basket. (Most US states do not use a shot clock for high schools; those that do must use 35 seconds.) Hitting the rim of the basket resets the shot clock, as do defensive fouls that do not occur in the act of shooting. If the offense lets the shot clock run out without shooting, a shot clock violation occurs, and the other team gets the ball.
Basketball players are not allowed to carry the ball as they move. This is called a traveling violation, and results in the other team getting the ball. Instead, the ball is passed between the players, and if a player is moving with the ball, the player has to dribble it, i.e. bounce it between their hand and the floor. A player is also not allowed to dribble the ball with both hands simultaneously, and doing so is a violation known as a double dribble that results in the other team getting the ball.
NBA
The National Basketball Association (NBA), the top league of basketball in the world, has 30 teams as of the 2022–23 season, one of which is from Canada and 29 from the United States. The NBA season begins in October and lasts until April, when a playoff series begins featuring the top 8 teams from the Eastern and Western Conferences. This culminates in June with the NBA Finals, where the conference champions meet to determine the NBA champion.
Eastern Conference
Atlantic Division
- Boston Celtics – TD Garden 📍, Boston, Massachusetts (in the North End). The Celtics have the most NBA Finals championships of any team, partially due to the greatness of Bill Russell and Larry Bird.
- Brooklyn Nets – Barclays Center 📍, Brooklyn, New York (in Downtown Brooklyn).
- New York Knicks – Madison Square Garden 📍, New York City, New York (in the Theater District).
- Philadelphia 76ers – Wells Fargo Center 📍, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania (in South Philly).
- Toronto Raptors – Scotiabank Arena 📍, Toronto, Ontario (in the Entertainment District).
Central Division
- Chicago Bulls – United Center 📍, Chicago, Illinois (on the Near West Side). Michael Jordan may be gone, but the Bulls still provide exciting games to watch.
- Cleveland Cavaliers – Rocket Mortgage FieldHouse 📍, Cleveland, Ohio (in Downtown Cleveland). The Cavaliers have finally won the championship that they — and their city — have longed for, but after LeBron James left for Los Angeles, the Cavs immediately plummeted to the bottom of the league. They've since returned to playoff contention behind a young nucleus.
- Detroit Pistons – Little Caesars Arena 📍, Detroit, Michigan (in Midtown Detroit).
- Indiana Pacers – Gainbridge Fieldhouse 📍, Indianapolis, Indiana.
- Milwaukee Bucks – Fiserv Forum 📍, Milwaukee, Wisconsin. Home to two-time league MVP Giannis Antetokounmpo.
Southeast Division
- Atlanta Hawks – State Farm Arena 📍, Atlanta, Georgia (in Downtown Atlanta).
- Charlotte Hornets – Spectrum Center 📍, Charlotte, North Carolina (in Uptown Charlotte).
- Miami Heat – Miami-Dade Arena 📍, Miami, Florida (in Downtown Miami).
- Orlando Magic – Amway Center 📍, Orlando, Florida.
- Washington Wizards – Capital One Arena 📍, Washington, D.C. (in the Penn Quarter).
Western Conference
Northwest Division
- Denver Nuggets – Ball Arena 📍, Denver, Colorado. Home to two-time reigning league MVP Nikola Jokić.
- Minnesota Timberwolves – Target Center 📍, Minneapolis, Minnesota (in Downtown Minneapolis).
- Oklahoma City Thunder – Paycom Center 📍, Oklahoma City, Oklahoma (in Downtown Oklahoma City).
- Portland Trail Blazers – Moda Center 📍, Portland, Oregon.
- Utah Jazz – Vivint Arena 📍, Salt Lake City, Utah.
Pacific Division
- Golden State Warriors – Chase Center 📍, San Francisco, California (on the Mission Bay waterfront). The Warriors have emerged as a "superteam" that has dominated the NBA, with such players as Steph Curry and Kevin Durant making the "Dubs" a team to contend with (though Durant has since departed, first for Brooklyn and now Phoenix). The Warriors returned to San Francisco in 2018 after nearly a half-century playing in Oakland, and after some injury-riddled seasons returned to the dominance of their recent past, winning the 2022 title.
- Los Angeles Clippers – Crypto.com Arena 📍, Los Angeles, California (in Downtown L.A.) The Clippers were historically known for being perennial underdogs, but have found some success starting around 2010, with the potential for even more with the arrival of Kawhi Leonard and Paul George in 2019.
- Los Angeles Lakers – Crypto.com Arena, Los Angeles, California (in Downtown L.A.) One of the most successful teams in the NBA's history, the Lakers are the team of Jerry West (whose silhouette appears on the NBA logo), Kareem Abdul-Jabbar, Magic Johnson, and Kobe Bryant. With LeBron James joining the team in 2018 and Anthony Davis joining a year later, they emerged from the doldrums of the previous 10 years, winning the title in 2020.
- Phoenix Suns – Footprint Center 📍, Phoenix, Arizona.
- Sacramento Kings – Golden 1 Center 📍, Sacramento, California.
Southwest Division
- Dallas Mavericks – American Airlines Center 📍, Dallas, Texas (in Downtown Dallas).
- Houston Rockets – Toyota Center 📍, Houston, Texas (in Downtown Houston).
- Memphis Grizzlies – FedExForum 📍, Memphis, Tennessee.
- New Orleans Pelicans – Smoothie King Center 📍, New Orleans, Louisiana (in the Central Business District).
- San Antonio Spurs – AT&T Center 📍, San Antonio, Texas.
WNBA
The Women's National Basketball Association (WNBA), operated by the NBA, is arguably the top women's league in the world, at least in level of competition. However, salaries greatly lag those on offer in major leagues in Europe and China (whose business models differ radically from those in the WNBA). Its season runs out of phase with the normal rhythm of basketball, being played over the Northern Hemisphere summer, when most other leagues (even those south of the equator) are on their offseason break. This scheduling was mainly to accommodate NBA team owners' desire for more arena dates during the offseason; when the WNBA was founded, all of the teams were owned by NBA franchises. Many of the teams have since been sold to outside owners, but the league has kept its summer schedule. This has the side effect of allowing many of the league's top players to play overseas during the traditional basketball season, usually making several times as much as they do in the WNBA.
The league's 12 teams, all in the US, are split into two conferences. In the upcoming 2023 season, each team will play 40 regular-season games. The top eight teams in the overall league standings, regardless of conference alignment, advance to the playoffs. The current playoff format, adopted in 2022, is a standard knockout format. The first round consists of best-of-three series, followed by the best-of-five semifinals and the best-of-five WNBA Finals.
Unlike other major sports in the US (except for soccer), and also unlike the NBA, the WNBA has a midseason tournament involving all of the league's teams. The Commissioner's Cup debuted in the 2021 season; it had been scheduled to debut in 2020 before COVID-19 got in the way. The first home and road game for each team against each of its conference opponents, all of which are played in the first half of the season, are designated as Cup games. Once each team has played all 10 of its Cup games, the teams with the best Cup record in each conference advance to the Cup final, a single game held immediately after the league completes its standard midseason break for either the All-Star Game or Olympics.
Eastern Conference
- Atlanta Dream – Gateway Center Arena 📍 in the Atlanta suburb of College Park, Georgia.
- Chicago Sky – Wintrust Arena 📍 on the Near South Side.
- Connecticut Sun – Mohegan Sun Arena 📍 at the Mohegan Sun casino complex in Uncasville, Connecticut.
- Indiana Fever – Shares Gainbridge Fieldhouse with the Pacers.
- New York Liberty – Shares Barclays Center with the Brookyln Nets.
- Washington Mystics – Entertainment and Sports Arena 📍 in the Congress Heights neighborhood of Southeast Washington, D.C.
Western Conference
- Dallas Wings – College Park Center 📍 on the campus of the University of Texas at Arlington.
- Las Vegas Aces – Michelob Ultra Arena 📍 at the Mandalay Bay casino on the Las Vegas Strip.
- Los Angeles Sparks – Share Crypto.com Arena with the Lakers and Clippers.
- Minnesota Lynx – Share Target Center with the Timberwolves.
- Phoenix Mercury – Shares Footprint Center with the Suns.
- Seattle Storm – Climate Pledge Arena 📍 at Seattle Center, just to the northwest of downtown Seattle.
Minor leagues
NBA G League
The NBA's official minor league, known as the G League due to a sponsorship deal with the Gatorade sports drink, has operated since 2001. It started with eight teams, all in the Southeast U.S., but it has steadily expanded over the years and now has 28 teams, each affiliated with a single NBA franchise (with most owned directly by the NBA team). It's expected that all 30 teams will have their own affiliates in the near future.
While the quality of play is obviously not as high as in the NBA, games are still intensely competitive—arguably more so than in the NBA, given that every player in the league is trying to prove himself to NBA teams. Also, the U.S. men's national team is now made up almost exclusively of G League players except in the final Olympic and World Cup tournaments.
The season is divided into two portions. It starts in November with the Showcase Cup, with a group stage followed by an 8-team knockout tournament. After the Showcase Cup ends just before Christmas, the regular season starts and runs through March, followed by playoffs that end with the G League Finals in April.
Each team's NBA affiliate is indicated in parentheses next to the team's name.
Eastern Conference
- Capital City Go-Go (Washington Wizards) – Entertainment and Sports Arena in the southeast Washington, D.C. neighborhood of Congress Heights, also home to the WNBA's Washington Mystics.
- Cleveland Charge (Cleveland Cavaliers) – Wolstein Center at Cleveland State University in downtown Cleveland.
- College Park Skyhawks (Atlanta Hawks) – Gateway Center Arena in College Park, Georgia, also home to the WNBA's Atlanta Dream.
- Delaware Blue Coats (Philadelphia 76ers) – Chase Fieldhouse in Wilmington.
- Fort Wayne Mad Ants (Indiana Pacers) – Allen County War Memorial Coliseum in Fort Wayne, Indiana.
- Grand Rapids Gold (Denver Nuggets) – DeltaPlex Arena in the Grand Rapids suburb of Walker, Michigan.
- Greensboro Swarm (Charlotte Hornets) – Greensboro Coliseum Fieldhouse, part of the Greensboro Coliseum Complex in Greensboro, North Carolina.
- Lakeland Magic (Orlando Magic) – RP Funding Center in Lakeland, Florida.
- Long Island Nets (Brooklyn Nets) – Nassau Coliseum in Uniondale, New York (on Long Island in Nassau County). Notably, this team plays in a former home of its parent club.
- Maine Celtics (Boston Celtics) – Portland Exposition Building in Portland, Maine.
- Motor City Cruise (Detroit Pistons) – Wayne State Fieldhouse at Wayne State University's athletic complex on Detroit's West Side, next to the boundary of Midtown.
- Raptors 905 (Toronto Raptors) – Paramount Fine Foods Centre in the Toronto suburb of Mississauga. Like its parent club, 905 is its league's only Canadian team.
- Westchester Knicks (New York Knicks) – Westchester County Center in White Plains, New York.
- Windy City Bulls (Chicago Bulls) – NOW Arena in the northwest Chicago suburb of Hoffman Estates, Illinois.
- Wisconsin Herd (Milwaukee Bucks) – Oshkosh Arena in Oshkosh.
Western Conference
- Austin Spurs (San Antonio Spurs) – H-E-B Center in the northwest Austin suburb of Cedar Park, Texas.
- Birmingham Squadron (New Orleans Pelicans) – Legacy Arena in Birmingham, Alabama.
- Iowa Wolves (Minnesota Timberwolves) – Wells Fargo Arena in Des Moines.
- Memphis Hustle (Memphis Grizzlies) – Landers Center in the Memphis suburb of Southaven, Mississippi.
- Oklahoma City Blue (Oklahoma City Thunder) – Paycom Center in downtown Oklahoma City, also home to the Thunder.
- Ontario Clippers (Los Angeles Clippers) – Toyota Arena in the Inland Empire city of Ontario, California.
- Rio Grande Valley Vipers (Houston Rockets) – Bert Ogden Arena in Edinburg, Texas.
- Salt Lake City Stars (Utah Jazz) – Lifetime Activities Center in the Salt Lake City suburb of Taylorsville, Utah.
- Santa Cruz Warriors (Golden State Warriors) – Kaiser Permanente Arena in Santa Cruz, California.
- Sioux Falls Skyforce (Miami Heat) – Sanford Pentagon in Sioux Falls, South Dakota.
- Stockton Kings (Sacramento Kings) – Stockton Arena in Stockton, California.
- South Bay Lakers (Los Angeles Lakers) – UCLA Health Training Center in the South Bay city of El Segundo, California.
- Texas Legends (Dallas Mavericks) – Comerica Center in the north Dallas suburb of Frisco.
In addition to the above, two teams are only playing exhibition games against other G League teams:
- Capitanes de Ciudad de México – A team from Mexico City that formerly played in that country's top professional league before joining the G League in 2021–22. Due to COVID-related border restrictions, the team chose to play only in the season-opening Showcase Cup, and is based in Fort Worth until the US–Mexico border fully reopens. Los Capitanes plan to fully join the league when COVID restrictions end.
- NBA G League Ignite – Established in 2020–21 as an NBA-sponsored one-year developmental program for elite high school players, providing an alternative to college basketball. The team, based in the East Bay community of Walnut Creek, California, only plays exhibitions against other G League teams.
College basketball (NCAA)
Most universities across the United States also sponsor basketball teams. Despite changes diminishing the role of colleges in developing talent, the collegiate game remains a major source of players for the NBA and WNBA. While there are several governing bodies for collegiate basketball, the most important of these is the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA). Teams are divided into conferences, which usually group universities in the same geographic region, and within the NCAA, divisions (the most prominent university programs compete in Division I) .
The collegiate season begins in early November, and ends in early March. After conference championships take up a week in mid-March, playoff tournaments determine national champions. In particular, the NCAA's Division I men's basketball championship, often called March Madness, generates intense fan and media interest. The single-elimination tournament lends itself to tension as stronger teams fight to avoid being upset by lesser known programs. The championship game occurs in early April.
More than 360 teams play within NCAA's Division I, with teams in every state but Alaska. Hundreds more play in lower levels of the collegiate game.
3x3
3x3 or three on three is a variant of basketball on a half-court with only one hoop and three players in each team. Under the rules of FIBA, which governs all play between national teams and whose rules are followed by almost all leagues outside the U.S., it's played in a single period of 10 minutes with a 12-second shot clock, and the team with the highest score when the time is up wins. Also, if one team reaches 21 points, the game is over and that team wins the game. Successful shots from within the arc are worth one point, from outside two points. Overtime in FIBA 3x3 is very different from that in the full-court game—it's an untimed period, although the shot clock still runs. Overtime ends once either team has scored two points. (This trumps the "21 points to a win" rule; if the game is tied at 20 at the end of regulation, it still takes two points to win.)
Developed in the 1980s in the United States, 3x3 has become an official form of basketball regulated by FIBA, and became a stand-alone Olympic sport in the 2020 Summer Olympics.
Streetball
.jpg/440px-Basketball,_Venice_Beach_(5749061286).jpg) Streetball is basketball played outdoors, and usually with less strict rules than regular basketball.
Streetball is basketball played outdoors, and usually with less strict rules than regular basketball.
Museums and other attractions
- Naismith Memorial Basketball Hall of Fame, Springfield (Massachusetts), 42.093684°, -72.585069°. A shrine to basketball in its birthplace. 2018-07-15
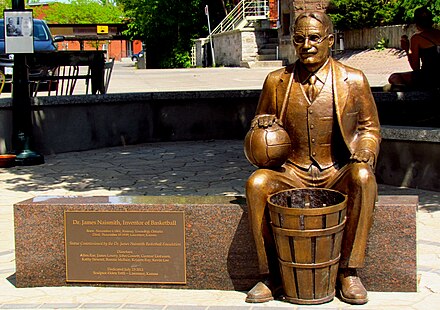
- Naismith Museum, Almonte (Ontario), Canada. Dr James Naismith who invented basketball grew up in the Almonte area. See also the Naismith Basketball Foundation. 2018-07-15
Outside North America
Outside North America, basketball is a big sport in Mediterranean Europe, the former Eastern Bloc, former Yugoslavia, China, the Philippines, and Liberia, and is the second most popular spectator sport in the world after soccer. International basketball rules differ slightly from the NBA, WNBA and NCAA rules, though these difference are largely minor, and top players are usually able to switch between rules without any major issues.
European men's club teams play each other in the EuroLeague (analogous to association football's UEFA Champions League), EuroCup (analogous to the UEFA Europa League), and Basketball Champions League (analogous to the UEFA Europa Conference League). Teams qualify for the EuroLeague and EuroCup through their respective domestic basketball leagues, some of the more notable ones being the leagues in Spain, Greece, Turkey and Russia, with their top basketball teams often being affiliates of their top soccer teams. European women's clubs have their own EuroLeague and EuroCup (which, unlike the men's versions which are run by the top clubs, are operated by FIBA's European zone).
The Philippines has a wildly popular professional league, the Philippine Basketball Association. Its business model radically differs from those of the NBA or European leagues—all teams are owned and operated by major local corporations, with teams changing their names almost every year to promote one or another of their owners' brands. No team has its own arena; all games are held at large arenas in Metro Manila. Its season is divided into three segments locally known as "conferences"—one restricted to players with Filipino nationality, and two that allow each team to field a severely restricted number of non-Filipinos. College/university basketball is also quite popular in the country, with numerous governing associations.
European men's national teams play each other in EuroBasket, a tournament now held every four years. FIBA's other continental zones have their own tournaments for men's national teams—Afrobasket for Africa, the FIBA AmeriCup for the Americas, and the FIBA Asia Cup for both the Asian and Oceanian zones. Each of these has an analogous women's tournament (which, unlike the men's versions, are still held every two years). Men's and women's national basketball teams from around the world play each other in the FIBA World Cup and in the Summer Olympics, with the Summer Olympics being considered the pinnacle of the sport for national teams. The men's World Cup is held the year before the Summer Olympics, and the women's version is in the same years as the Winter Olympics and FIFA World Cup. The United States is by far the dominant team in international basketball, having won the vast majority of gold medals at the Olympics in both the men's and women's events.