California - state of the United States of America
There is a statewide health emergency due to the mpox virus (formerly known as monkeypox), with most cases concentrated in Los Angeles and San Francisco. For more information, see the California Department of Public Health mpox website.
Perhaps the most diverse of all the fifty states in the Union, California has a culture ranging from the easygoing surf spots on the beaches of Southern California to the glamor of Hollywood, and the counterculture and thriving businesses of the Bay Area. The state, which is on the west coast of the U.S., also varies greatly in natural beauty, from redwood forests on the North Coast to the ski resorts of the rugged Sierra Nevada mountains and the harsh desert of Death Valley. The largest state in the U.S. by population and one of the largest by area, California boasts world-famous attractions and sights: Disneyland, the Golden Gate Bridge, the Napa Valley wine country, and the tallest mountain in the contiguous United States, Mount Whitney.
Regions
California is geographically varied, ranging from warm beaches to snowy mountains to fertile farmland to extreme desert. In the middle of the state is the farmland of the Central Valley, which provides produce to the whole country. The conventional wisdom is that there is a huge difference—and also rivalry—between the Southern California area around Los Angeles (or as Californians often say, “LA”) and Northern California centered around the San Francisco Bay Area. However, the contrast between the (relatively wealthy) urban coastal areas and the (relatively poor) suburban and rural Central Valley is just as pronounced, if not more so.
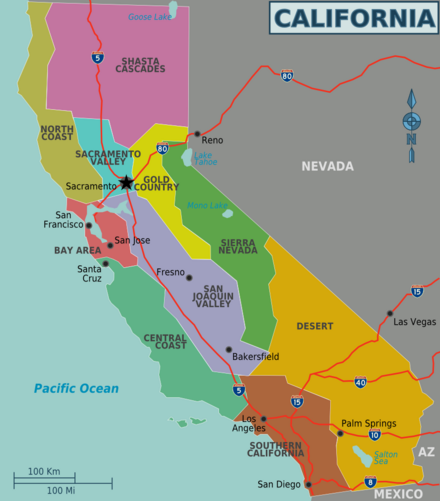
Home to the world's tallest trees, the coast redwoods, as well as rugged coastlines and remote nature adventures.
Lakes and mountains off the beaten path in the state's northeast corner.
Home of Sacramento, the state capital, and the urban areas around the city.
Historic foothills leading east to the Sierras; the 1848 discovery of gold in this region brought many Americans to California and helped California become a state less than five years after the territory had been acquired.
California's alpine and skiing region, including Yosemite National Park and Lake Tahoe.
Home to the cities of San Francisco, Oakland, and San Jose, as well as the technology-centered Silicon Valley and sophisticated Wine Country.
Breadbasket of California and home to a large percentage of America's fruit and vegetable supply.
An isolated stretch of land that features cool mountains and a rugged coastline.
Home to the metropolis of Los Angeles, as well as San Diego, Disneyland, and miles of famous beaches.
Cities
 Here are a few of California's most notable cities.
Here are a few of California's most notable cities.
- Eureka 📍 – former logging town with charming Victorian city center, waterfront trails, and Redwood Sky Walk featuring the world's tallest tree species.
- Redding 📍 – Sundial Bridge and gateway to a plethora of outdoor adventures ranging from underground caverns to some of the highest volcanic peaks in the United States.
- Sacramento 📍 – the laid-back state capital with historic Gold Rush-era quarter of the city, Old Sacramento.
- San Francisco 📍 – Golden Gate Bridge, Alcatraz, America's largest Chinatown, cable cars, and Victorian houses.
- San Jose 📍 – south of San Francisco, this city is the center of Silicon Valley, and is home to many technology companies and the (in)famous Winchester Mystery House.
- Santa Barbara 📍 – city on a south-facing coast which styles itself, with some justification, as "the American Riviera."
- Los Angeles 📍 – the state's largest city, and 2nd-largest in the nation. L.A. is home to Hollywood, Venice, The Getty Center, and Griffith Park.
- Palm Springs 📍 – desert recreation with golf, spas, resorts, casinos, and the famous aerial tramway.
- San Diego 📍 – Balboa Park, Old Town, SeaWorld, San Diego Zoo, and nearby Tijuana, Mexico.
Other destinations
- Big Sur 📍 can be loosely defined as the stretch of coastline between Carmel and San Simeon, and the steep cliffs, rocky coast, churning waves, abundant wildlife, redwoods, and remoteness make it a stunningly beautiful drive.
- Death Valley National Park 📍 – a place of legend and a place of trial.
- Disneyland 📍 – this world-famous amusement park opened its doors in 1955 and today draws around 16 million yearly visitors. The California Adventure theme park was added in 2001 and provides attractions inspired by the state's scenery and movie industry.
- Hearst Castle 📍 – former ornate estate of media mogul William Randolph Hearst, perched atop a hill overlooking the Pacific Ocean.
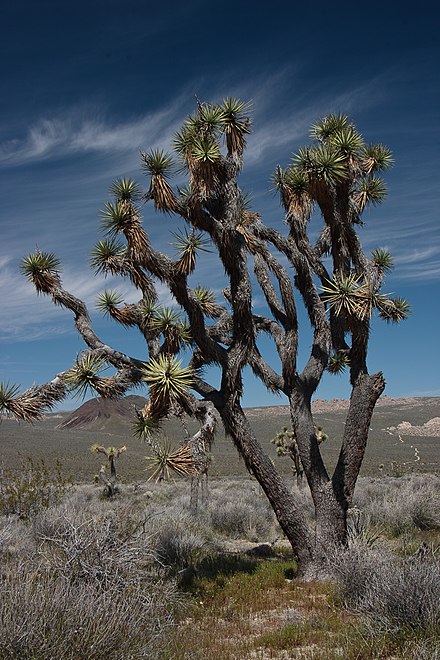
- Joshua Tree National Park 📍 – combines two different desert ecosystems anchored by the peculiar-looking namesake tree species.
- Lake Tahoe 📍 – a deep blue mountain lake, popular for water sports in the summer and skiing in the winter.
- Napa Valley 📍 – spas, wine tasting, wine tours; the historic heart of California Wine Country.
- Sequoia and Kings Canyon National Parks 📍 – these twin parks hold monuments to nature's size, beauty, and diversity, including the largest tree on Earth, the General Sherman Tree.
- Yosemite National Park 📍 – one of the first wilderness parks in the United States, the site of natural wonders such as Half Dome, El Capitan, and numerous waterfalls.
California also has many state parks, approximately half of which are near urban centers.
Understand

History
See also: Indigenous cultures of North America
Human settlement in California goes back 50,000 years; California was home to thirty different tribal groups prior to the arrival of European explorers in the 1500s and now over 120 tribes are left. The first Europeans to discover what is now California were the Spanish and Portuguese. Spanish colonialism was established through twenty-one missions built throughout California by the late 1700s. These missions still survive today, stretching from San Diego on the Mexican border to Sonoma in the northern San Francisco Bay Area.
After the Mexican War for Independence in 1821, California became a part of Mexico for 25 years until 1846, when many of its residents declared a sovereign nation (the California Republic, also known as the Bear Flag Republic) before it was annexed by the United States in 1846, and has since then had an image as the "land of opportunity" and the final destination of luck-seekers. In 1848, the discovery of gold in the Sierra Nevada mountains kicked off the California Gold Rush, and California's non-native population surged from 15,000 to over 300,000 within two years. People who moved to California during the Gold rush were often called "49ers", a term that was adopted as the name for the San Francisco football team. California became a state in 1850, and its population has increased steadily since then.
Los Angeles, a city which once boasted one of the longest streetcar networks in the world, boomed through defense contractors and later converted to a "freeway" city after the streetcars were dismantled. The city hosted Olympic Games twice (1932 & 1984) at times when the Olympic movement was in crisis and the games were largely seen as successes for the city as well as the Olympic movement. In the post-war years, California (especially the Bay Area) became a hotspot of counterculture, including popular music, the anti-war movement, and the LGBT community. Since the late 20th century, the state and in particular, the Bay Area, has been at the forefront of the Digital Revolution, with innovations such as personal computers to smartphones having been introduced through Silicon Valley.
Today California is the most populous state in the US with over 38 million residents and still growing rapidly. Taken by itself California would rank as one of the world's top ten economies and Californian places like Silicon Valley, Hollywood and San Francisco are known globally and have shaped not only American but world culture. Politically, California is seen as a solidly "blue" state: it has a two thirds majority of Democrats in both chambers of the legislature and often provides the Democratic party with particularly left-wing ideas, especially on social issues. That said, the state actually contains a lot of political diversity, with conservative views prevalent in much of the state outside the densely populated Bay Area and Los Angeles County, particularly in the fertile but relatively sparsely populated Central Valley.
Landscape
 With over 160,000 square miles (411,000 km<sup>2</sup>), the landscape of California is vast and varied, and the stereotypical beach paradise is only the tip of the iceberg. The state contains extremes in elevation, with Mount Whitney at 14,505 ft (4,421 m) being the tallest mountain in the lower-48 states, while less than 200 miles away Death Valley, at 282 ft (82 m) below sea level, is North America's lowest point.
With over 160,000 square miles (411,000 km<sup>2</sup>), the landscape of California is vast and varied, and the stereotypical beach paradise is only the tip of the iceberg. The state contains extremes in elevation, with Mount Whitney at 14,505 ft (4,421 m) being the tallest mountain in the lower-48 states, while less than 200 miles away Death Valley, at 282 ft (82 m) below sea level, is North America's lowest point.
California's border to the west is made up of a rugged coastline along the Pacific Ocean. The coastal mountains rise up from the ocean and are home to redwood trees in the northern half. The Central Valley bisects California from north-to-south before giving way to the Sierra Nevada mountains, home of Yosemite National Park, Sequoia and Kings Canyon National Parks and other natural wonders. The southeastern part of California is dominated by desert, which covers 25% of California's total area. The Mojave is a high desert, with elevations ranging from 3,000 to 6,000 ft (1,000 to 2,000 m) above sea level. This area receives less than six inches (152 mm) of rain each year.
Climate
 The state's climate varies from subtropical at the coast to the brutal winters of the mountains to one of the world's hottest regions in the deserts. Rainfall is more common in the northern part of the state than in the south, and snow is rare except in the mountains. Most precipitation occurs during winter, but California experiences frequent droughts. This has prompted people to install drought-resistant landscaping. In some years, farms lie fallow due to lack of water for irrigation.
The state's climate varies from subtropical at the coast to the brutal winters of the mountains to one of the world's hottest regions in the deserts. Rainfall is more common in the northern part of the state than in the south, and snow is rare except in the mountains. Most precipitation occurs during winter, but California experiences frequent droughts. This has prompted people to install drought-resistant landscaping. In some years, farms lie fallow due to lack of water for irrigation.
The hottest temperature ever recorded in the Western Hemisphere, 134°F (56.6°C) was at Death Valley in 1913, and temperatures here regularly exceed 120°F (50°C) during the summer. In contrast, winter temperatures in the mountains can drop below 0°F (-20°C). In between these extremes there are great local variations in climate due to topography and the influence of the Pacific Ocean upon precipitation and temperature, with temperatures becoming increasingly moderated nearer the coastline.
For swimming, the Pacific Ocean can be surprisingly cold even in July due to currents. September and October are the best months for swimming. Another surprise in coastal areas is the presence of cool temperatures and fog in the mornings through most of the year. To experience California as a sunny place, plan to sleep late.
People
California is a very diverse state with many ethnic groups. California has large populations of people of varied backgrounds such as Mexican, Salvadoran, Guatemalan, Armenian, Iranian, Jewish, Chinese, Russian, Filipino, Eastern Indian, Korean, Japanese, Vietnamese, Cambodian, Thai, and Hmong. California also has large populations of African Americans and Native Americans.
Although typically considered to be a liberal state, Californians have a wide variety of political views which tend to vary based on region. The Central Valley, Orange County, San Diego, and Palm Springs area tend to be more conservative, while Los Angeles County and the San Francisco Bay Area are among the most progressive areas in the country.
California is a large and diverse state, with different cultures in each region.
Holidays
California observes all the federal holidays, except Columbus Day, and adds Cesar Chavez Day on March 31st (or nearest weekday). However, some cities such as Coronado that have a large population of federal workers or military personnel do observe Columbus Day.
Get in

By plane
See also: Flying in the United States
San Francisco International Airport (IATA: SFO) and Los Angeles International Airport (IATA: LAX) are the most popular entry points with a wide variety of flights from Europe, East Asia, India, Oceania (Australia, Fiji, New Zealand, Tahiti, etc.), Latin America and from various cities in the U.S. on a variety of U.S. and foreign flag carriers. To a lesser extent there are also direct flights from the Middle East (Israel, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Turkey, UAE) to Los Angeles. They are however also the most crowded and the SFO-LAX route is one of the busiest air corridors in the world causing frequent delays due to congestion. Delays at San Francisco airport due to fog are also somewhat common. If coming from within the U.S. and from Mexico there are other alternate airports in California that are less crowded and may be closer to your final destination. They are:
- Los Angeles area – [Hollywood-Burbank Airport (Bob Hope Airport)](http://hollywoodburbankairport.com/) (IATA: BUR) in [Burbank](Burbank#By_plane) (closest to Hollywood and Downtown Los Angeles), [John Wayne Airport](http://www.ocair.com) (IATA: SNA) in [Orange County](Santa_Ana_(California)) (closest to Disneyland & Knott's Berry Farm), [Ontario Airport](Ontario_(California)#By_plane) (IATA: ONT) in Ontario (closest to Joshua Tree and the Inland Empire deserts), and [Long Beach Airport](http://www.lgb.org) (IATA: LGB) in [Long Beach](Long_Beach) (west coast hub for JetBlue Airlines).
- San Francisco Bay Area – [Oakland Airport](http://www.flyoakland.com) (IATA: OAK) in Oakland (closer to Downtown San Francisco than SFO), [San Jose Airport](http://www.sjc.org) (IATA: SJC) in San Jose (closest to Silicon Valley), and [Sonoma County Airport](https://sonomacountyairport.org/) (IATA: STS) in [Santa Rosa](Santa_Rosa_(California)) (closest to Wine Country); both San Francisco and Oakland airport are now connected to the local metro network, BART while San Jose is connected by Caltrain via a free shuttle to the 'Santa Clara Station'.
- [San Diego Airport](San_Diego#By_plane) (IATA: SAN) in San Diego
- [Sacramento Airport](Sacramento#By_plane) (IATA: SMF) in Sacramento
- [Reno Airport](Reno#By_plane) (IATA: RNO) in [Reno](Reno), Nevada is closer to the Lake Tahoe area than from Sacramento.
- [Fresno Airport](http://www.flyfresno.com) (IATA: FAT) in Fresno, closest to Yosemite NP.
- Palm Springs (IATA: PSP)
- Central Coast – Monterey (IATA: MRY) (closest to Big Sur), San Luis Obispo (IATA: SBP) (closest to Hearst Castle), and Santa Barbara (IATA: SBA).
- [Las Vegas Airport](Las_Vegas#By_plane) (IATA: LAS) in Las Vegas, Nevada is closer to Death Valley NP than from Los Angeles or Ontario.
- [Tijuana Airport](Tijuana#By_plane) (IATA: TIJ) in Tijuana. If coming from Mexico it may be more advantageous to fly to Tijuana on a (Mexican) domestic flight and then cross into San Diego by ground transportation than on an international flight to San Diego, Los Angeles, or other cities further north. From San Diego, you can continue north to the San Francisco Bay area, Las Vegas, [Phoenix](Phoenix) or wherever in the U.S. you are continuing to. See [By plane](California#By_plane_2) under the "Get Around" section for more information.
By train
See also: Rail travel in the United States
Amtrak serves several routes into and out of California. If you are going to Los Angeles from the Central Valley, you might have to change to a bus for the last part of the trip, as the only railway connection between the Central Valley and Los Angeles is also one of the busiest freight lines in the USA. Plans to build a new high speed rail line to link San Francisco and Los Angeles are underway, but completion is not scheduled before the late 2020s.
The following Amtrak routes serve California and terminate in Los Angeles or Emeryville:
- The California Zephyr runs daily between Chicago and Emeryville with connections in Omaha, Denver, Provo, Salt Lake City and Reno/Lake Tahoe. This train also stops in the Sierra Nevada (Truckee and Colfax) and the Sacramento Valley (Roseville, Sacramento, Davies and Martinez). Emeryville is the nearest Amtrak station to downtown San Francisco where passengers transfer to the Amtrak Thruway bus to continue across the bay to San Francisco.
- The Coast Starlight runs daily between Los Angeles and Seattle via Portland, Klamath Falls, Redding, San Francisco Bay Area, Santa Barbara, San Luis Obispo and Oxnard.
- The Southwest Chief runs daily from Chicago via Kansas City, Albuquerque, Flagstaff, Williams Junction (nearest stop to the Grand Canyon) and Kingman to Los Angeles. It also makes stops in the Mojave Desert (Needles, Barstow and Victorville); the Inland Empire (Riverside and San Bernardino) and Orange County (Fullerton) and on its way into Los Angeles.
- The Sunset Limited runs three times a week from New Orleans via Houston, San Antonio, El Paso, Tucson and Yuma. Additionally, Amtrak's Texas Eagle service between San Antonio and Chicago incorporates the Sunset Limited to provide a direct connection to Los Angeles with the same stops as the Sunset Limited between San Antonio and Los Angeles. This train also stops in the Inland Empire (Pomona, Ontario and Palm Springs).
Train services are limited to two token lines with hardly any real transport value in Mexico and there are NO passenger rail service to anywhere near the U.S./Mexican border from anywhere in Mexico.
By bus
Many bus companies operate services to California. Service is most frequent along the interstates from large cities in neighboring states. See By bus under Get around in the below for a list of bus companies serving the state.
By car
All major road entrances (including entrances from other U.S. States) to California have agricultural inspection stations to ensure that some fruits and vegetables do not cross into a region where they may come into contact with the farms in the Central Valley. Often, travelers are subject to border inspection (somewhat strict for domestic travel) and asked if they have been on a farm or are carrying organic matter with them.
Get around
California is the third largest state of the U.S. by area (after Alaska and Texas). It compares in size with Sweden. However, getting around California can be simple.
By car

 In addition to interstates and US highways, California has one of the most expansive state highway systems in the United States. As with all long-distance trips in the United States, a car is generally the best way to get around and see destinations, especially rural ones. However the trip from the northern end of California to the southern end can take well over ten hours as the state's varied and in places rugged terrain can pose obstacles to the road network. The coast routes (State Route 1 and U.S. 101) are much slower and windier than Interstate 5, and GPS travel estimate times may be inaccurate, especially on Highway 1.
In addition to interstates and US highways, California has one of the most expansive state highway systems in the United States. As with all long-distance trips in the United States, a car is generally the best way to get around and see destinations, especially rural ones. However the trip from the northern end of California to the southern end can take well over ten hours as the state's varied and in places rugged terrain can pose obstacles to the road network. The coast routes (State Route 1 and U.S. 101) are much slower and windier than Interstate 5, and GPS travel estimate times may be inaccurate, especially on Highway 1.
Most California drivers are courteous and careful (although speeding is rampant), and the safety and ease of driving in California is comparable to most wealthy countries. Exceptions may be found in the most congested areas of San Francisco and Los Angeles — where potholes, road rage and reckless driving are commonplace — and some country roads in mountain ranges. Information about vehicle collisions and other non-congestion traffic problems on highways are reported online at chp.ca.gov/traffic. Traffic congestion is tracked by most online map sites.
Gasoline prices are more expensive than in other parts of the U.S.; consider public transit in highly populated areas such as the Bay Area where prices are especially high.
Freeway signage (and cautions)
California uses the MUTCD (Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices) lane marking system standard throughout the United States, in which dashed white lines divide lanes of through traffic and yellow divides opposing traffic (with single dashed indicating passing and double solid indicating no passing). In many urban areas the lane markings are replaced by Botts dots for additional tactile feedback when crossing lanes.
The network of freeways in major population centers is often confusing and intimidating to those unfamiliar with the area, so having a good map is very helpful. The great majority of exits from freeways are on the right. At interchanges between freeways, in most cases, the flow of traffic continues through the left lanes with the transition to the other freeway being in the right lanes.
At certain freeway interchanges, Caltrans (California Dept. of Transportation) is notorious for posting advance direction signs that do not correctly explain which lanes correspond to which ramps. Additionally, Caltrans does not always post signs warning of upcoming lane drops or merges.
For example, where a freeway has three through lanes and the central lane splits into two lanes, thus resulting in two ramps with two lanes each, the advance signage may incorrectly imply that only the right lane will break off for the upcoming right-side ramp, thus causing visitors driving in the middle lane to merge unnecessarily into the right lane. And the two lanes on the right-side ramp may suddenly merge into each other without any warning.
These issues frequently result in visitors making wild last-minute lane merges. The 2009 national MUTCD is intended to remediate this problem (as seen in California and several other states) by mandating the use of detailed arrows on direction signs that clearly show which lanes split into new lanes at upcoming interchanges, but California has not yet implemented the new MUTCD standard. Thus, one should approach major freeway interchanges in California with caution.
Mile-based exit numbering is in progress but is still very erratic in areas; an exit number may not be marked at all, may be marked on the last directional sign before the exit, or may be marked on the final "EXIT" sign where the exit ramp separates.
Ramp meters
In urban areas, the access ramps to a freeway may have traffic lights for each lane (called ramp meters or ramp metering lights; you'll see warning signs that read "METER ON"). During high-traffic times, the traffic light spaces out the vehicles attempting to merge onto the freeway. Be sure to read the sign below the light as ramps can allow 1 to 3 vehicles per green light. Most ramp meters are for ramps from local roads to a freeway, but some freeway junctions have meters on their ramps too.
Toll roads and bridges
Most highways are freely accessible, although there are a handful of tollways as well as tolled lanes on roads that are otherwise freeways. Most Southern California toll roads have no toll plazas; in most cases, you must have a FasTrak account and transponder - see below - to drive and pay the toll. On the other hand, all major bridges in the San Francisco Bay Area have toll plazas, with tolls charged on traffic in only one direction. All Bay Area toll plazas have cash lanes, except the Golden Gate Bridge (which takes photos of the license plates for non-FasTrak vehicles and bills the owner later). Cash toll lanes are staffed by human toll collectors; California toll plazas do not have "exact change" lanes where drivers may toss change in a basket without stopping.
All California toll roads and toll plazas also accept FasTrak electronic toll collection transponders (aka tags) which can be used throughout the state. FasTrak is not compatible with any other state's ETC system. Going through a FasTrak-only toll plaza lane or toll road without a transponder or (only in some cases) an active FasTrak account with which your car's license plate is registered will result in a very expensive ticket.
HOV/carpool lanes
Some freeways have a high occupancy vehicle (HOV) lane on the far left. This lane, also called the carpool lane or diamond lane, is marked by:
- a diamond symbol painted on the road surface
- signage on the wall separating the two sides of the freeway, with the diamond symbol
- a double yellow line on the road surface (only in Southern California) Some freeway access ramps have carpool lanes too; often, the non-carpool lanes will have ramp meter traffic lights while the carpool lane has none.
In most cases, the carpool lane is only for vehicles with 2 or more persons inside, motorcycles, and clean-air vehicles with government-issued "Access OK" stickers. Sometimes, 3 or more persons and/or a FasTrak transponder may be required, so check the signage before entering a carpool lane. Carpool lane restrictions may be enforced 24 hours a day every day, or only when the signage says so (in those cases, it's usually only during rush hour on weekdays).
Carpool lanes in Southern California have limited access points marked by a dashed white line. This is the only point at which a vehicle may legally enter or exit a carpool lane, since you are not allowed to cross a double yellow line.
The minimum fine for unlawful use of a carpool lane is $490.
Traffic safety and law enforcement
All persons in a moving vehicle are required to wear a seatbelt and the driver and all passengers can be individually ticketed for failing to do so. Motorcycle riders must wear a helmet. Cellphone users are required to use a hands-free headset if talking on the phone while driving. Texting by the driver is illegal, as is any action on the phone that forces the driver to touch it more than once (and even single-touch actions are only allowed if the phone is mounted securely rather than hand-held). Unless otherwise signed, right-turns are permitted at red lights following a full stop. If it is raining hard enough to require you to use your windshield wipers, California law requires that your headlights be turned on.
California does not have stationary photo radar cameras to deter speeding like in other countries, and mobile manned photo radar units are rare and still experimental. However, most California police officers do carry radar guns and use them often, and on rural freeways, the California Highway Patrol occasionally flies aircraft overhead to spot speeders and help ground units home in on their positions. Red light enforcement cameras are in use at many urban intersections, but are usually marked only by a single "PHOTO ENFORCED" sign before the intersection. The cameras must obtain a clear view of the driver's face and license plate before a ticket may be issued.
California's laws against driving under the influence of alcohol are very strict; the maximum permissible blood alcohol concentration is 0.08%. All drivers are strongly encouraged to call 911 to report drunk drivers.
California requires disabled out-of-state visitors to apply at the Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) for a travel placard for handicapped parking. It's valid for 90 days.
Travelers with a non-US driver's license are generally permitted to drive in California. However, travelers who are in California for more than 10 days with some kinds of visas, especially the K-1 non-immigrant visa for future spouses, have run into some difficulties over their place of residence. The DMV refuses to issue drivers' licenses to people with non-immigrant visas, but police have filed charges against some of them for becoming a California resident without promptly obtaining a California license – the very license that the State refuses to issue on the grounds that they haven't legally become residents yet. This risk may be reduced by giving your non-California address as your place of legal residence if stopped by police.
Unlike most states, "lane-splitting" by motorcyclists (i.e. riding down the painted lines between traffic lanes) is legal in California and commonly done in heavy traffic. It's only legal when traffic is going slower than 30 mph, and motorcyclists are only allowed to go 15 mph faster than the general flow of traffic, but many motorcyclists seem to treat this as more of a guideline than a hard and fast rule. As a result, if you're driving a car, take extra care to watch for motorcycles when changing lanes on a major highway.
Major highways
 Here are some important highways in California:
Here are some important highways in California:
- Interstate 5: Runs between San Diego, Los Angeles, and Sacramento, then north into Oregon and Washington
- Interstate 8: Runs between San Diego and Arizona
- Interstate 10: Runs between Los Angeles, the Inland Empire and Palm Springs, then into Arizona and points east
- Interstate 15: Runs between San Diego, the Inland Empire, Barstow, Las Vegas, Nevada and points north
- Interstate 40: Runs between Barstow, Needles, then into Arizona and points east
- Interstate 80: Runs between the Bay Area, Sacramento, Reno, Nevada, and points east
- Interstate 405: Runs through the center of the Los Angeles Area
- Interstate 580: Connects the San Francisco Bay Area with Interstate 5 in the Central Valley
- State Route 1: Runs up the California Coast between Orange County, Los Angeles, Monterey, the Bay Area, and Fort Bragg
- State Route 99: Runs along the California Central Valley between Red Bluff, Sacramento, Stockton, Modesto, Fresno and Bakersfield
- U.S. Highway 50: Runs between Sacramento, South Lake Tahoe, Carson City, Nevada, and points east
- U.S. Highway 101: Runs between Los Angeles, Santa Barbara, then close to the California Coast to the San Francisco Bay, Eureka and points north
- U.S. Highway 395: Runs along the Eastern Sierras, connecting the Inland Empire and High Desert with Bishop, Reno, and Susanville, then into Oregon and points north
- Route 66: Now decommissioned, historically connected Los Angeles, the Inland Empire, Barstow, Needles, then into Arizona and points east
By plane
 Flying may be a more reasonable option for crossing large expanses of the state. American/American Eagle; United/United Express, Delta, Southwest, JetBlue, Jet Suite X (JSX) and Alaska Airlines offer intrastate flights within the state of California. San Francisco is a hub for United and Alaska; Los Angeles is a hub for United, American/American Eagle, and Alaska Airlines; and Long Beach is the West Coast hub for JetBlue. The LAX-SFO route is one of the busiest in America which means competitive fares and delays are frequent which is only made worse by the fog that tends to hit San Francisco bay on a regular basis. In addition, the airlines offer flights from different airports in southern California in the south; to the SF Bay area and Sacramento to the north at competitive rates.
Flying may be a more reasonable option for crossing large expanses of the state. American/American Eagle; United/United Express, Delta, Southwest, JetBlue, Jet Suite X (JSX) and Alaska Airlines offer intrastate flights within the state of California. San Francisco is a hub for United and Alaska; Los Angeles is a hub for United, American/American Eagle, and Alaska Airlines; and Long Beach is the West Coast hub for JetBlue. The LAX-SFO route is one of the busiest in America which means competitive fares and delays are frequent which is only made worse by the fog that tends to hit San Francisco bay on a regular basis. In addition, the airlines offer flights from different airports in southern California in the south; to the SF Bay area and Sacramento to the north at competitive rates.
The primary airports served by major US carriers, Volaris (from Mexico) and Aeromexico (from Mexico) in California are in:
- Los Angeles area – [Los Angeles International](Los_Angeles_International_Airport) (IATA: LAX), [Burbank-Hollywood Airport (Bob Hope Airport)](http://hollywoodburbankairport.com/) (IATA: BUR) in [Burbank](Burbank#By_plane), [John Wayne Airport](http://www.ocair.com) (IATA: SNA) in [Orange County](Santa_Ana_(California)); [Ontario Airport](Ontario_(California)#By_plane) (IATA: ONT), and a small airport in [Long Beach](http://www.lgb.org) (IATA: LGB)
- San Francisco Bay Area – [San Francisco](San_Francisco_International_Airport) (IATA: SFO), [Oakland](http://www.flyoakland.com) (IATA: OAK), [San Jose](http://www.sjc.org) (IATA: SJC), and [Sonoma County Airport](https://sonomacountyairport.org/) (Charles M. Schulz Airport) (IATA: STS) in Santa Rosa; both San Francisco and Oakland airport are now connected to the metro, BART, while San Jose is connected by Caltrain via a free shuttle at the 'Santa Clara Station'. Oakland is closer to Downtown San Francisco than SFO is and offers a fog-free alternative.
- [San Diego](San_Diego#By_plane) (IATA: SAN)
- [Sacramento](Sacramento#By_plane) (IATA: SMF)
- [Reno](Reno#By_plane) (IATA: RNO), Nevada closer to the Lake Tahoe area than Sacramento
The busiest second tier airports are Fresno (IATA: FAT) (nearest to Yosemite NP); Santa Barbara (IATA: SBA); and Palm Springs (IATA: PSP). There are also flights from major hubs to Arcata/McKinleyville (nearest to Eureka), Bakersfield, Crescent City, El Centro, Mammoth Lakes, Merced, Monterey, Redding, San Luis Obispo, Santa Maria, and Stockton.
By train
The state's various rail services provide a cheap and reasonably comfortable way to see and get around much of the state without a car. Amtrak operates a few long-distance routes through and out of California, as well as the three Amtrak California (dead link: January 2023) routes:
- San Luis Obispo-Santa Barbara-Los Angeles-Anahiem-San Diego on the _[Pacific Surfliner](https://www.pacificsurfliner.com/)_
- Oakland/Sacramento-Stockton-Fresno-Bakersfield on the _[San Joaquins](https://amtraksanjoaquins.com/)_ (which have connecting Thruway bus service to Los Angeles)
- San Jose-Oakland-Sacramento-Auburn on the _[Capitol Corridor](https://www.capitolcorridor.org/)_
- Los Angeles-Santa Barbara-San Luis Obispo-San Jose-Oakland-Sacramento-Redding-(continues to Seattle) on the _Coast Starlight_
- Emeryville (San Francisco connection)-Sacramento-Truckee (near Lake Tahoe)-(continues to Chicago) on the _California Zephyr_
- Los Angeles-Palm Springs-(continues to Chicago) on the Sunset Limited
- _Amtrak Thruway Motorcoaches_ connects additional cities and towns to/from the Amtrak (train) network by bus such as Santa Cruz-San Jose; San Francisco-Emeryville; Bakersfield-Los Angeles; Bakersfield-Las Vegas; Martinez-Arcata; Redding-Sacramento; etc.
Amtrak has seen continuously increasing ridership in most of the USA for more than a decade now, and surprisingly enough three of the six most popular Amtrak routes run through California, thus making them a viable alternative to the more often than not congested roads and airports.
In addition, there are several commuter and regional services in the state's metro areas:
- _[Caltrain](http://www.caltrain.com)_ San Francisco-Palo Alto-San Jose-Gilroy through the famous Silicon Valley.
- _[Altamont Commuter Express](http://www.acerail.com/)_ San Jose-Stockton through the Altamont Corridor Express.
- _[BART](http://www.bart.gov/)_ operates in the Bay Area, connecting much of the East Bay (Oakland, Berkeley, Walnut Creek) to San Francisco and SFO.
- _[Metrolink](http://www.metrolinktrains.com/)_ runs regional train service throughout the greater Los Angeles, Orange, Riverside, San Bernardino and Ventura County (metropolis) region on multiple routes.
- _[COASTER](http://www.gonctd.com/coaster)_ runs along the coast of San Diego County between downtown San Diego, Carlsbad and Oceanside.
- _[SPRINTER](https://gonctd.com/services/sprinter-hybrid-rail/)_ runs across Northern San Diego County between Escondino and Oceanside with bus and train connections to Los Angeles and San Diego.
- _[Sonoma-Marin Rail (SMART)](https://www.sonomamarintrain.org/)_ runs between Santa Rosa and San Rafael in Marin/Sonoma County (Northern Bay Area) with ferry connections to San Francisco
There are also light rail systems in San Diego, Los Angeles, San Francisco, Sacramento, and San Jose. Almost all of these systems are being expanded or upgraded to cope with rising ridership, so expect more and better service in years to come.
By bus
See also: Long-distance bus travel in the United States
The bus is not the most glamorous way to get around the state, but it can be the cheapest. There are fairly frequent service from Los Angeles to San Francisco/San Jose; San Diego/Tijuana; Las Vegas/San Bernardino and Sacramento with on multiple routes with various bus companies. There are other the smaller companies, county bus services, and those connecting rural towns which are not listed, check the article of your destination for all the transportation options. Information on transit can be found here.
- Eastern Sierra Transit, +1 760 872-1901. Operates 'local' buses along US Hwy 395 corridor between Mammoth Lake, Bishop and Lone Pine in Mono and Inyo Counties in the eastern 'Desert' and the Sierra Nevada parts of the state. They have a route continuing north to Carson City & Reno from Mammoth Lake and south to Lancaster from Lone Pine. The area is not served by Greyhound or Amtrak Thruway buses 2016-12-08
- El Paso Los Angeles Limousine Express, (downtown LA depot) 622 E 6th St (SW corner of E 6th St & Wall St across the street from police station), +1 213 623-2323 and +1 323-265-3232. Travels along I-10 between Los Angeles, Indio, Phoenix, Las Cruces and El Paso on one route and on I-15 to Las Vegas & North Las Vegas on another route. They have additional stops in E. Los Angeles, El Monte and Colton on their way on both routes. They also have a second depot at 4425 S Atlantic Blvd in E Los Angeles. 2016-04-10
- Flixbus, +1 855 626-8585. German bus company to rival Greyhound Lines (First Group); Megabus (Stagecoach Group) and various American and Mexican bus companies in the American market. It connects Los Angeles to Las Vegas, Phoenix, Sacramento, SF Bay Area and San Diego via multiple cities en route in Arizona and California. It may expand to other parts of the U.S. if it is successful. It dominates the German market and has grown rapidly through subcontracting its operations, which has the downside for customers that the buses are not of a consistent style or quality. 2018-06-14
- Green Tortoise, +1 415 956-7500. Operates something like a 'hippie' bus that serves as a bus by day with stops to visit different places like a bus tour throughout the day and a RV camper by night in different campgrounds. It offers bus tours and camping trips to Joshua Tree, Yosemite, Death Valley Sequoia and along the coast between San Francisco and Los Angeles. Some of its tours involve a 3- to 5-day round trip from the point of origin such as from San Francisco to Yosemite NP and back while others are one way where the journey starts from one place and end in the other like from Los Angeles to Joshua Tree and end in Las Vegas. Even with round trips it is possible to ask to be picked up or dropped off in different places than the point of origin/return. Others like its 'Hostel Hoppers' or 'Express' are a straightforward bus ride from point A to B. It is one way to combine 'taking the bus' from one place to another and to visit and see remote places without a private automobile. 2016-05-22
- Greyhound & Cruceros-USA. Greyhound goes to 100 locations statewide, though these are not all actual stations, some are merely stops. In general, Greyhound serves the same routes that Amtrak does along the main highways. In some cases Greyhound is cheaper, faster, and more frequent than Amtrak. 2016-04-10
- Hoang Express, +1 714 839-3500. Travels between SoCal (San Diego, El Monte, Los Angeles, Westminster); Bay Area (San Francisco, San Jose & Oakland) and to Sacramento on another route from Los Angeles. They also offer service from Los Angeles to Arizona (Phoenix, Chandler and Tempe. $60-65 to Bay Area; $80 to Sacramento
- International Bus Lines (formerly Intercalifornias), +1 213 629-4885. Connects Tijuana, San Ysidro (just over the border), Santa Ana, Los Angeles, San Fernando, Bakersfield, Fresno, and San Jose/Stockton (route splits/joins in Madero) and several other places in between. Prices vary depending on your destination
- LuxBus, on request for hotel pick up/drop off. Operates to/from Las Vegas, Anaheim, and San Diego.
- Mendocino Transit Authority (MTA). Travels extensively in the North Coast region along Hwy 1 from Ft Bragg to Navarro River Junction (#65), Point Arena (#75), Bodega Bay and Santa Rosa (#95). Another route from Ft Bragg to Willits, Ukiah and Santa Rosa along SR-20 and US Hwy 101 (Rt #65). Much of the area is not served by Greyhound or Amtrak Thruway Buses off the US Hwy 101 corridor. 2016-12-08
- Megabus. Goes to Las Vegas from Los Angeles. They also have another route from San Francisco to Sacramento along I-80. 2021-08-05
- Orange Belt Stages (Trailways), +1 559 733-4408. Regular scheduled service between Lenmoore and Santa Maria through Paso Robles and San Luis Obispo. They also offer day trips (dead link: December 2020) to different places for sightseeing and to scheduled events throughout California. 2018-06-09
- Sage Stage, (bus stops) Rite Aide @ 5th & Main in Alturas, +1 530 233-6410. Provides public transportation from Alturas and Canby in Modoc County, in the Shasta Cascades, to Redding; Reno, NV; and Klamath Falls, OR on three separate routes. 2016-12-18
- Santa Barbara Airbus, +1 805 964-7759. Eight trips a day from LAX to Carpinteria, Santa Barbara and Goleta. 2021-08-05
- "Cabin" (formerly Sleep Bus). Overnight service to the Los Angeles area (Ocean & Arizona Ave in Palisades Park in Santa Monica) from San Francisco (Bayside Lot @ 1 Bryant St). This is an actual sleeper bus featuring twin size bunk beds with privacy curtains, power outlets, and free wifi. 2016-04-25
- Tufesa, +1 213 489-8079. Connects Los Angeles to Sacramento (via Bakersfield, Fresno, etc); to Salt Lake City (via Barstow, Las Vegas, St George, etc); to Hermosillo (via Phoenix, Tucson, Nogales); San Francisco Bay Area; and to Tijuana (via Santa Ana, San Diego/San Ysidro). Prices vary depending on your destination 2022-11-30
- Yarts. Operates regularly scheduled buses from Yosemite NP (Visitors' Center) to Fresno, Merced, Mammoth Lakes & Sonora on four separate routes. 2016-05-22
By foot
- The Pacific Crest Trail crosses the length of California on its way from Mexico to Canada
- The American Discovery Trail connects California with Nevada and the East Coast.
By boat
- Ferry service is limited, but can be a scenic, relaxing, and fun way to travel. Major services exist in the Bay Area, to the Channel Islands and to Catalina Island near Los Angeles. Several of the smaller coastal towns have water taxi services within their city. Check as the stops and limited and the schedules may seasonal.
- Many cities are along the coast, or else on navigable waterways, and you can dock your own boat there.
Talk
 Although the California Constitution states that English is the official language of the state of California, in reality, California is a multilingual state. American English is the main language and Spanish is the de facto second language, and a knowledge of even rudimentary Spanish is useful in most cities from Sacramento to San Diego. Los Angeles has some of the largest Hispanic populations north of Mexico. The state is highly influenced by Spanish culture due to its history, and it is not uncommon to see store and street signs written in both English and Spanish. "Spanglish" (a mixture of English and Spanish) is often used and heard throughout the state. Even people with no Latino heritage whatsoever sometimes speak fluent Spanish or use common Spanish-derived expressions when speaking English. Most government offices and tourist attractions, as well as many businesses in California have at least a few employees who are bilingual in English and Spanish. Some restaurants in fact may have a workforce that is more fluent in Spanish than English.
Although the California Constitution states that English is the official language of the state of California, in reality, California is a multilingual state. American English is the main language and Spanish is the de facto second language, and a knowledge of even rudimentary Spanish is useful in most cities from Sacramento to San Diego. Los Angeles has some of the largest Hispanic populations north of Mexico. The state is highly influenced by Spanish culture due to its history, and it is not uncommon to see store and street signs written in both English and Spanish. "Spanglish" (a mixture of English and Spanish) is often used and heard throughout the state. Even people with no Latino heritage whatsoever sometimes speak fluent Spanish or use common Spanish-derived expressions when speaking English. Most government offices and tourist attractions, as well as many businesses in California have at least a few employees who are bilingual in English and Spanish. Some restaurants in fact may have a workforce that is more fluent in Spanish than English.
Due to a history of Asian immigration and influence, Asian languages such as Cantonese, Mandarin, Tagalog, Vietnamese, Korean, Japanese, and Hindi are also spoken among Asian Californian populations. The major cities also tend to have communities of essentially any ethnicity imaginable, and there is a good chance you can hear their language and have an opportunity to experience their cultures. San Francisco, for example, is home to a significant French community, while Los Angeles boasts quite a large Ethiopian neighborhood.
See
 As the most geographically and culturally diverse state in the U.S., California offers an endless amount of things to see and do; even when you think you've experienced everything in one area of the state, a short trip to another part has plenty more to offer.
As the most geographically and culturally diverse state in the U.S., California offers an endless amount of things to see and do; even when you think you've experienced everything in one area of the state, a short trip to another part has plenty more to offer.
Incredible and unique scenery, some of the most recognizable landmarks in the world, centuries old historical sites, unending cultural and entertainment options no matter where your interests lie, California will almost certainly offer it.
Natural attractions
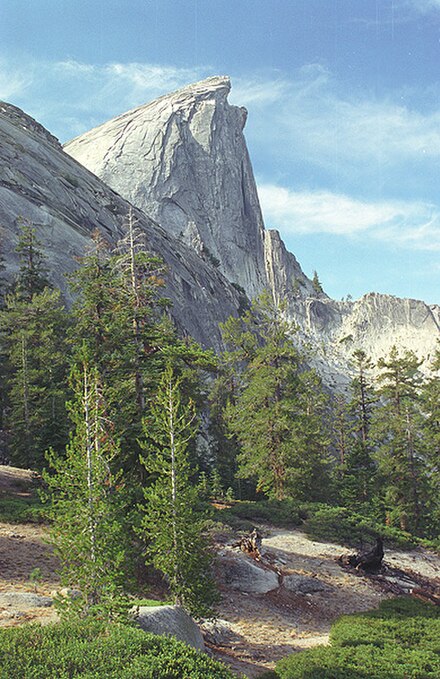 From white-sand beaches to snowcapped mountains, with lush forests and arid deserts in between, no other state offers such a wide a variety of natural landscapes as California does.
From white-sand beaches to snowcapped mountains, with lush forests and arid deserts in between, no other state offers such a wide a variety of natural landscapes as California does.
California hosts the largest number of U.S. national parks with a total of nine. The most famous of these is Yosemite National Park, featuring thundering waterfalls and geological behemoths like El Capitan and Half Dome. The surrounding Sierra Nevada also hosts nearby Sequoia and Kings Canyon National Parks which are both home to some of the world's largest living organisms, the giant sequoia. Redwood National Park in the far northwestern corner of the state and the surrounding area feature the world's tallest species of trees, the coast redwood.
Tired of forests? The California desert is the site of some the hottest and most arid places on Earth. Death Valley National Park is the location of the highest ever recorded temperature on the planet. If deserts are not your thing, beaches and California are practically synonymous. Big Sur and Point Reyes are notable examples of a scenic, winding stretch of unspoiled coastline that is typical of Northern California, featuring rocky cliffs and towering redwood trees that meet thundering ocean waves. Further south, the water is much warmer and suitable for all-day beach trips. Here, world-class beach towns such as Santa Barbara, Malibu, and those of Orange County offer opportunities to catch waves, practice beach volleyball, or simply lounge around and tan underneath palm trees.
If high-altitude adventure is what you are seeking, California has that too. At an elevation of 14,505 feet (4,421 meters) above sea level, Mount Whitney is the highest mountain in the lower 48 states. Snow activities such as skiing and snowboarding are plentiful in Lake Tahoe in the winter, while hiking and water recreation such as boating are popular in summer.

While the national parks may receive most of the attention, California has the largest state park system in the United States. These protected areas are found in places ranging from being adjacent to national parks to green landscapes in the middle of cities that offer a respite from the hectic urban rush.
California's high population and its climate have also led to the creation of numerous reservoirs.
California marine animals (native and migrating) are easily found find in the wild along the state's beaches, in lagoons and estuaries, such as sea otters, grey whales, elephant seals, harbor seals, sea lions as well as multitudes of tide pools dwellers including crabs, sea stars, anemone, and sea urchins. Timing is key: go at low tide to see lots of marine life.
Monuments and architecture
California has long been a canvas for architects and engineers to design and build some pioneering structures or to popularize styles that would define a time period. With two of the most prominent cities in the United States, Los Angeles and San Francisco, this is certainly notable with many of the structures and buildings that are found there.
San Francisco is home to engineering marvels such as the Golden Gate Bridge, Lombard Street (the most crooked street in the world), and cable cars that seemingly glide up and down the hills between the waterfront and rest of downtown. The many skyscrapers such as the Transamerica Pyramid have all been specifically designed to withstand powerful earthquakes. The stately Palace of Fine Arts and charming Painted Ladies of Alamo Square have served as backdrops countless of times for the City by the Bay.
As the epicenter of the global entertainment industry, the Hollywood Sign is an icon of Los Angeles recognized worldwide. The nearby Hollywood Walk of Fame, Capitol Records Building, and numerous theaters all solidify the city's hold on entertainment. The Griffith Observatory and Walt Disney Concert Hall are also notable features in the cityscape, as is the imposing Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum, the site of the 1932 and 1984 Summer Olympics.
Other notable landmarks outside these two cities include the California State Capitol in Sacramento (modeled after the U.S. Capitol in Washington, D.C.), labyrinthine Winchester Mystery House in San Jose with eerie origins, and the lavish Hearst Castle in the Central Coast town of San Simeon that anchors the landscape of the surrounding area.
Historical sites
From former Native American sites to suburban garages where modern technology was invented, California's centuries-long history is preserved in numerous historical sites and museums that are scattered throughout the state.
One of the most comprehensive collections of state history from prehistory to contemporary times is housed in the Oakland Museum of California in Oakland, with a vast collection of nearly 2 million items related to California history, art, and science.
The legacy of Spanish colonial times remains with the string of twenty-one missions that span the length of much of the state from Mission San Diego de Alcalá in the San Diego's Old Town (founded in 1769) up to Mission San Francisco Solano in the Bay Area town of Sonoma (founded in 1823). Perhaps the most beautiful of these though, is Mission Santa Barbara, which lent its name to the same city and is rightfully referred to as the "Queen of the Missions".
El Pueblo de Los Angeles Historical Monument in downtown Los Angeles is another historical feature from the Spanish era, although the neighborhood underwent a major transformation during the period of Mexican rule (1821 to 1848) that now gives the area a distinct Mexican atmosphere, particularly along Olvera Street.
Spain was not the only European power that colonized California, however. Fort Ross in the northern edge of the Bay Area was the southernmost Russian outpost in North America and was in operation from 1812 to 1841.
Gold Rush legacies live on in Gold Country, located in the northeastern part of the state. Following the discovery of gold at Sutter's Mill in Coloma in 1848, hundreds of thousands of fortune seekers from around the world made their way to California, establishing dozens of towns, most of which still retain their Old West charm and atmosphere. Old Sacramento in the state's capital city also sprung up as the commercial and transportation center of this era, with places of interest including the first terminus of the First Transcontinental Railroad and related California Railroad Museum.
Cannery Row and much of the rest of Monterey provide a glimpse of the state's once lucrative fishing and canning industry during the first half of the 20th century, with carefully preserved wooden buildings that housed factory workers and engines, along with rustic (and still active) piers.
Itineraries
- El Camino Real (The Royal Road) — a historic road linking the 21 Spanish missions of Alta California (modern day state of California) offering a fascinating look into California's history
- Pacific Coast Highway — tour up and down the iconic California coast, along Big Sur, all the way up to its end where it merges into the US 101, which goes up to Washington state.
Do

- Ski at one of the great resorts near Lake Tahoe or Big Bear.
- Try your hand at surfing or work on your tan in Orange County or Santa Monica.
- The long coastline offers some great California scuba diving.
- Go winetasting at one of the countless vineyards dotting Wine Country.
- Climb a mountain and camp in the Sierra Nevada or Shasta Cascades.
- See California's amazing wildflowers. From March through May, the California Wildflower Hotline at +1 818 768-3533 offers the latest information on the best places to view wildflowers throughout Southern and Central California. The hotline and website are updated every Thursday evening. More than 90 wildflower sites are included. The hotline, founded in 1983, is run by the Theodore Payne Foundation for Wild Flowers and Native Plants.
- Listen to music at the Northern California Blues Festival. The fastest growing festival of its kind comes in June to Sacramento County around Father's day each year and usually features a spectacular line-up of Blues artists. Event benefits Through the Mind, a non-profit providing free alternative mental health to America's Veterans.
- Visit one of the many theme parks, such as Disneyland or Six Flags Magic Mountain.
Buy
Usually US dollars and common credit or debit cards are the only accepted modes of payment. Many stores can take contactless payment methods such as Apple Pay and Google Pay. You might have some luck with Mexican Pesos near the immediate border area, but the exchange rates are usually pretty bad.
California stores no longer give out free plastic bags, except for fresh grocery produce and meats. Reusable plastic bags cost a minimum of ten cents (by state law). Many stores sell cloth bags for one or two dollars. Sales tax varies from county to county and city to city; it is usually around 9% and is charged on almost everything except regular groceries.
The quintessential California souvenir depends a lot on which part of the state you visited, and what your interests are. The agricultural products change from citrus and avocadoes down south to strawberries in the middle, to almonds and wine as you move north. In LA, you might take home chocolates from See's Candies; in the Central Coast, keep an eye open for locally produced saltwater taffy; in the Bay Area, it's all about Ghirardelli Chocolate. Common themes for souvenir items include surfing, tie-dyed clothing, and redwood trees.
Eat
See also: American cuisine
California doesn't have a single, well-defined cuisine of its own, but rather has a remarkably diverse food scene defined by its large population of immigrants of varied ethnic backgrounds and its access to one of the most productive agricultural regions on this side of the planet. The culinary style referred to as Californian cuisine or California fusion focuses on imaginative fusions of other cuisines, typically with heavy attention to presentation and an emphasis on using freshly prepared local ingredients, and has been somewhat subsumed into the general trend of "New American" cuisine.
Almost any dish you can imagine can be found somewhere in California, with the cuisines of the Americas and Asia heavily represented, and those of nearly every other country available to a lesser extent. More "North American" fare includes everything from burger shacks to vegetarian, organic and even completely vegan restaurants; the Californian love for food has made it one of the most diverse restaurant scenes in North America. The large cities have the most variety, while things get simpler and more meat-heavy as you get more rural.
There are a handful of distinctive California dishes, although most of them have been adopted and adapted throughout the US.
- Cobb salad – a cold salad of bacon or ham, chicken, boiled eggs, avocado, tomato, lettuce, and bleu cheese, with a vinaigrette dressing. Traditionally it's chopped fairly fine, but in modern times it's served in a variety of ways, and sometimes with ranch dressing instead of the traditional vinaigrette. It was invented at the Brown Derby restaurant in LA.
- French dip sandwich – invented somewhere in LA, the exact location is subject to dispute, but it's a warm sandwich of thinly sliced roast beef on a roll that's dipped into beef broth.
- Cioppino – a seafood stew developed by Italian immigrants in San Francisco, it resembles various Italian fish stews but includes local ingredients like chopped Dungeness crab.
- The Mission Burrito – a San Francisco tradition characterized mainly by its great size and caloric content, featuring copious amounts of beans and rice in addition to cheese, meat and/or vegetables.
- California Burrito – a San Diego specialty, it's a carne asada (spicy grilled steak) burrito, stuffed with french fries.
- Santa Maria Barbeque – This is a central coast tradition. It's a bottom sirloin beef roast (the cut is locally known as tri-tip), where the fat hasn't been trimmed. It's suspended high above a hot oak fire, fat side up, so it cooks slowly and the fat melts and tenderizes the meat. It's usually served thinly sliced with tortillas or bread, salsa, onions, avocado, and other side dishes.
- Chop Suey – the original "American Chinese" dish was popularized as cheap food for laborers during the California gold rush. While it's increasingly hard to find, many other American Chinese dishes were first created in San Francisco's Chinatown. Larger cities in California have some restaurants selling American Chinese food and others selling traditional Chinese dishes. In smaller cities, the Americanized version may be the only option on the menu. As a general rule, plain water is free at any restaurant. However, if you need a disposable cup, the cup will cost you 25 cents (by state law). You are allowed to bring your own reusable water cup or bottle.
Regional chains
California's classic burger chain In-N-Out has expanded to states as far east as Texas—see Fast food in the United States and Canada for more. Outside of fast food, California chains that you'll be hard-pressed to find elsewhere include:
- Ike's. Casual sandwich joint with more than 50 locations, mostly in California though a few are in Nevada. The menu varies by location, but in general about half the menu has meat and half is vegetarian; many vegetarian options can be made vegan. The sandwiches are filling and flavorful but not excessively heavy. 2019-06-22
- Three Twins Ice Cream. You can buy their ice cream at supermarkets and convenience stores all over the country, but the ice cream shops are only in California (plus a few new branches in Japan and Korea). Organic ice cream with somewhat distinctive flavors. They usually have a couple of vegan/non-dairy options.
- Farmer Boys. A farm-to-table restaurant chain featuring a burger shack menu that is freshly cooked from local produce. Hamburgers, sandwiches, and salads, plus diner-style breakfast options served all day. 2021-10-17
- Lemonade. Poke bowls, chef bowls, sandwiches, and 10 different types of freshly made lemonade. This is California fusion food without the high-end budget. Take your friend who's always bored with the same-ol' stuff. Don't neglect the side dishes. Vegan options. $15 2021-10-17
Drink
California is known for its fine wine and gourmet beers. Napa, Sonoma and Mendocino are premier wine districts north of San Francisco, but there are others in the Central Coast region and even the San Diego region where suitable microclimates have been found. The inland Central Valley region has hotter summers and traditionally produced inexpensive bulk wines, but quality has been improving with winemaking innovations.
For beer, California also has a lot of microbreweries. Sierra Nevada, in Chico, is one of the biggest microbreweries in North America. In the Central Coast the mid-sized brewery Firestone Walker in Paso Robles is a good addition to the local wineries in the area. In San Diego, Stone Brewing Company offers a great variety of beers that can be purchased throughout the state. There are over 200 microbreweries in California.
Legal issues
Californians tend to view wine as a natural accompaniment of food or socializing, overlooking its alcoholic content more easily than with distilled spirits. However police crackdowns on drinking and driving are noticeable, with roadblocks and random checks. Conviction for driving with a blood alcohol level over .08 percent is likely to bring serious legal and financial consequences. Drivers with a lower blood alcohol can still be convicted for DUI (driving under the influence) if they fail field sobriety tests, such as walking a straight line.
You must be 21 years of age to buy or drink any alcoholic beverage. Underage drinking is taken very seriously, so if you want a drink and appear to be under 30, you should be ready to present identification showing your age. The only acceptable proof-of-age documents are passports from any country, and identity documents issued by US government agencies (e.g., drivers' licenses issued by any US state). Foreign drivers' licenses and foreign identity cards are not legally acceptable as proof-of-age documentation, and people who are unable to produce a passport or valid United States ID will be refused service. Only original identity documents will be accepted; photographs or photocopies will not be accepted.
Stay healthy
Air pollution
While air pollution levels have dropped dramatically since the 1970s, more than ninety percent of Californians live in counties with unhealthy air. Visitors to the mountains or the rural regions of Northern California will have nothing to worry about, but the overreliance on cars, low rainfall, and surrounding mountains in Los Angeles, the Central Valley, and the Bay Area create some of America's worst air quality. It gets particularly bad when a layer of cold air gets "trapped" by a layer of warmer air above it ("inversion") which is particularly likely in basins. While air quality is rarely at levels that would be considered immediately dangerous, visitors should heed alerts and be especially cautious when any local wildfires are burning.
Occasionally, there will be an advisory issued for air stagnation, which is a phenomenon involving an air mass that cannot move and therefore stagnates over an area for an extensive period of time. Air pollutants can cause breathing difficulties for those with existing respiratory conditions.
If you have a respiratory condition, refer to the National Weather Service website on air quality to see if any such advisories have been issued for the areas you might visit.
Disease
_(5-29-09)_cerro_alto_campground_road%2C_slo_co%2C_ca_-01_(3577515146).jpg/440px-MOUSE,_CALIFORNIA_(peromyscus_californicus)_(5-29-09)_cerro_alto_campground_road,_slo_co,_ca_-01_(3577515146).jpg)
Deer mice can transmit a virus that causes hantaviral pulmonary syndrome. You are most likely to get infected if you breathe in dust containing their excrement (feces, urine, and saliva). Realistically, however, hantavirus is of very little concern to the traveler, as only a few people get infected each year, and most of them are exposed on the job, but sensible precautions should be applied. Do not venture in any wild animal's den or touch deer mice or their excrement. If you need to clean up after rodents, wear waterproof gloves, eye protection, and a high-quality respirator mask, and use disinfectants and wet-mopping techniques, rather than brooms and vacuums (both of which spread virus-laden dust). If you do get infected, treatment usually involves a week or two in the hospital. The main defense against the virus is prevention.
Stay safe

California–Mexico border
Due to California's proximity to the international boundary with Mexico, visitors should be cautious while in areas near the border.
- Beware Customs and Border Patrol (CBP) checkpoints and patrols. CBP is legally allowed to stop you or your vehicle solely in order to inquire about your citizenship and residency status within 100 miles of any international border (in this instance, the US–Mexico border). Non-whites, and especially Latinos, should expect to be profiled, targeted, and harassed by these government agents.
- Know where you are at all times. Follow good safety procedures and use common sense when making decisions.
- Do not pick up hitchhikers. If the person is undocumented or carrying drugs, you could be mistaken for a trafficker.
- Keep valuables, including spare change, out of sight and lock your vehicle.
- Avoid traveling in well-marked but unofficial "trails."
- Avoid hiking or camping in areas of major border activity. If you are visiting a national or state park, consult park staff to help plan backcountry travel in safer areas.
Crossing the border
Thousands of U.S citizens visit the state of Baja California, Mexico from California every year, with the majority of travelers returning from an enjoyable experience. However, a minority of travelers do experience difficulties and serious inconveniences while traveling to Mexico. Before traveling to Mexico, ensure that you have the proper documentation and are familiar with the recommendations for foreign travel from the U.S. Department of State, Bureau of Consular Affairs (dead link: January 2023)
There are six border crossings between California and Mexico: two between San Diego and Tijuana, one between Tecate and Tecate, two between Calexico and Mexicali, and one between Andrade and Los Algodones. The United States operates a consulate-general in Tijuana and a consulate in Mexicali. Mexico operates Consulates in Calexico, Fresno, Los Angeles, Oxnard, Sacramento, San Bernardino, San Diego, San Francisco, San Jose and Santa Ana.
Crime
The usual inner city crime can be found in the worst parts of Los Angeles, San Francisco, and Oakland. Central Valley cities, such as Sacramento, Stockton, and Fresno also have gang problems. Northern coastal cities such as Eureka have an ongoing problem with significant drug activity and property crimes. However, most California cities are safe. As long as you take basic precautions against petty crime, such as keeping your phone and other valuables out of sight in tourist areas, and stay out of obviously run-down neighborhoods, you will probably have a safe and pleasant visit.
If you are traveling along the Pacific Coast Highway or Highway 101, you may notice there are a substantial number of hitch-hikers along the way. Most are harmless youthful travelers or people who just need to get somewhere for lack of other means, while others may be a bit less safe to pick up. Use your best judgement, and, unless you feel confident in the people to whom you're giving a ride, it's probably better not to offer one while you're travelling alone.
Drugs are illegal in California, with the noted exception of marijuana. Adults 21 and over are allowed to possess, use, and cultivate small amounts of marijuana, so long as it is not consumed in public or possessed on the grounds of a school or day care center. The maximum amount a person may possess is one ounce of marijuana or 8 grams of concentrates. Some dispensaries sell marijuana products to the general public, although others remain restricted to those who have a medical marijuana recommendation from a doctor. Delivery services are also available. Marijuana is still illegal under federal law, so do not carry marijuana across state lines—even to another state where it is legal—as this will be considered drug trafficking and subject to harsh punishment. Also, do not take marijuana onto federal land, including any of the dozens of national parks and national forests in California.
If you find yourself in an emergency situation (of any kind), dial 9-1-1 on your phone or from any (available) phone. It is a free call from a payphone.
Earthquakes
Earthquakes that are large enough to cause extensive damage are rare, but remain a matter of reality for the state. Most earthquakes are mild and last for a couple of seconds. You're not likely to encounter one during your trip, but if you do, you'll probably go home with nothing more exciting than a story about it being over before you figured out that it was an earthquake. Compared to Japan, where earthquakes are common and a smartphone-based earthquake alert system is well-developed, or Mexico City, whose geography makes earthquakes easier to predict, expect to have no or very little warning even if you sign up for mobile-based alerts. When you feel the shaking, drop, cover, and hold on.
The biggest dangers in an earthquake are falling objects (such as books or bottles flying off shelves – or the whole shelf with all of its contents, if it's not properly mounted) and windows, which may shatter explosively. In the event of an earthquake, face away from windows and hide under any sturdy table or desk – and then hold on to that table, because the shaking could cause the table to slide across the floor. Contrary to popular belief, do not stand in a door frame; these are structurally weaker spots in modern buildings, and they provide no protection against falling objects.
If you are indoors, do not run outside! Falling building facades are more likely to cause severe injuries than anything inside. If outdoors, stay away from buildings (especially brick chimneys, which may spray bricks around a large area), and stay out from under power lines.
If you are driving, your first thought will probably be that something is wrong with your car. Immediately slow down and then stop at the nearest safe place. When the shaking is over (the ground and your nerves), it's okay to start driving again, but drive cautiously, as traffic signals will likely be out, the road surface may be cracked, other drivers may be panicking, and there may be trees or damaged vehicles blocking the road ahead.
Deserts
Along the southern most border of California-Nevada, as well as the border of California-Arizona, California has elaborate desert landscapes which extend into the south central regions of the state, the most famous (or infamous) being the region known as Death Valley, where several tourists and hikers have indeed met their fate while exploring the region.
If you are planning on traveling or hiking into these locations, follow desert survival guidelines. Be sure to take plenty of water (at least one gallon/four litres per person, per day), sunscreen and wear light clothing. Let someone know where you are going and when you expect to return.
Be sure to have a full tank of gasoline prior to traveling by car into these regions, as many desert locations are extremely remote and without any services for several miles (in some cases nearly 100 miles). To break down in these regions could be extremely unpleasant in the best case scenario, tragic in the worst.
Also, it is best to hike during the earlier part of the day, as thunderstorms tend to develop suddenly during the afternoon. In the event you encounter inclement weather conditions, seek high ground immediately! Thunderstorms can cause flash flooding in canyons and other low-lying areas.
Tsunamis
The incidence of earthquakes in California raises the concern for potential threats of tsunamis. Though tsunamis occur very rarely, a great deal of California's coastline is in a tsunami zone. For more information on the state's hazard assessment, visit the NOAA Center for Tsunami Research website.
Wildfires
Wildfires are common between May and October, but can also occur at other times.
Precautions include the following: clear the area around campfire pits/rings in campgrounds, never leave flames unattended (even artificial ones), do not throw cigarette ends out of a car, and avoid unnecessary weapon use in dry areas.
The strongest impact from fires is smoke. Smoke affects areas dramatically exceeding the size of the root fire. Travelers with respiratory issues should consult visitor information sites before visiting areas where fires are occurring, or anywhere in the path of the smoke, which can spread across large portions of the state during the worst wildfires.
Mudslides
Fire season is followed by the rainy season, and hilly areas where the vegetation has burned are particularly vulnerable to destructive and sometimes deadly mudslides. Heed any evacuation warnings that are issued.
Wild animals
Bears are found in the Sierra Nevada and all neighboring parts of the state. They're rarely dangerous, but should never be approached. If you are camping, you need to ensure that food, food waste, and other scented items such as soap and toothpaste are secure from them. Mountain lions are rarely seen, but live in all mountainous parts of the state and once in a while attack humans. If you see one, yell and wave your arms to make yourself appear as large as possible. Coyotes are quite common, even in relatively populated areas like the Hollywood Hills. They pose little danger to humans, but will attack dogs, cats and other domestic animals. Many animals, most notoriously bats, can carry rabies. When hiking, watch for ticks, which can carry Lyme disease, and rattlesnakes. California is home to 2 potentially deadly species of spiders - the black widow and the brown recluse - if you don't go poking around abandoned structures and woodpiles, you're very unlikely to encounter them. If you're bitten by any animal, seek immediate medical attention. Shark attacks have happened once in a great while at California beaches, and deadly sharks such as great whites do roam the California coast, but unless a shark has been repeatedly sighted by a specific beach (the local media will broadcast warnings) this is an extremely remote possibility.
Poisonous plants and mushrooms
Poison oak can be found almost anywhere in the state, but is particularly common in Southern California, the Central Coast, the Bay Area, and any Coast Redwood woodlands. It's toxic throughout the year, even during the winter when it's lost its leaves. Sensitivity varies by individual, but many people can end up with a very nasty, blistering rash by contacting it. See the linked article for treatment options. California is also home to several lethal varieties of mushrooms, which can be particularly dangerous to would-be gatherers because some of them resemble edible varieties found elsewhere in the world. Even if you're an expert on mushroom varieties where you live, don't assume you're safe gathering them in California.
Respect
California is filled with a very diverse group of people. Northern and Southern California have notably different cultures, while the rural areas in the Central Valley and Eastern portions of the state differ even more significantly. Sensitive topics include immigration, water rights, and land-use. Los Angeles and the San Francisco Bay Area are especially well-known for being some of the most politically liberal areas in the US, and continue to serve as some of the world's major centers of counterculture. Conversely, parts of California, particularly the Central Valley, are conservative. However, don't assume any individual's political leaning based on where they live.
Go next
- Arizona – Home to the Grand Canyon, Arizona borders California to the southeast across the Colorado River.
- Nevada – California's eastern neighbor is best known as the home of Las Vegas, although towns such as Reno and Carson City are also good day-trip opportunities for visitors wanting to explore the Silver State.
- Oregon – Sharing a border to the north, Oregon is home to impressive mountains and extensive forests.
- Hawaii – Many visitors to America's fiftieth state depart through California on their journey across the Pacific, but it is not a neighboring state and requires a 5-hour flight to get there.
- Baja California – Those traveling across the border to Mexico can visit some of that country's most impressive sea and landscapes.
Related: Off-road vehicles in California
Related: California desert camping
California
ca.govUnited States
usa.govPopulation:327.2 MDial code:+1Currency:Dollar (USD)Voltage:120 V, 240 V, 60 HzNEMA 14-30NEMA 14-50
